Für viele Menschen klingt es wie Science Fiction. Doch die Wettermanipulation ist ein alter Traum der Menschheit, der sicherlich Jahrtausende alt ist. Sei es zum Abwenden von Unwetterkatastrophen oder um den für die Landwirtschaft so wichtigen Regen herbeizuzaubern. Seit 1891 sind wissenschaftlich-technische Patente belegt, die sich mit der Wettermanipulation beschäftigen. Findige Internetnutzer haben sie gesammelt – wir bieten sie zur Eigenrecherche an.
Sie finden nachfolgend eine Liste von Patenten aus verschiedenen Patentdatenbanken, die sich mit der Herstellung künstlicher Wolken oder der Veränderung des Wetters beschäftigen. Die Existenz eines Patentes bedeutet nicht automatisch, dass der beschriebene und erwünschte Effekt auch tatsächlich funktioniert. Normalerweise reicht man aber ein Patent ein, weil man davon ausgeht, dass es funktioniert und dass der Patentinhaber damit gutes Geld verdienen kann – speziell unter Berücksichtigung der US-amerikanischen Mentalität.
Ein paar Beispiele:
Systeme und Methoden, um Regenwolken zu erzeugen, 2021
Die Patentschrift von Frederick William MacDougall aus San Diego umfasst zahlreiche technische Zeichnungen. Sie befasst sich mit dem Erzeugen von Regenwolken in geringer Höhe auf Basis von Wasservorkommen auf der Erde, seien es Meere, Seen oder Flüsse.
Die Systeme oder Methoden können als Mittel des Geoengineerings beschrieben werden, erklärt der Patentinhaber. Sinn ist es, Regen zu erzeugen, um Dürre und Waldbrände zu vermindern und zudem die Luft zu reinigen. Ein kühlender Effekt im Hinblick auf “menschengemachte Erderwärmung” wird versprochen. Die beschriebene Methodik ist technisch sehr aufwändig und komplex. Im Grunde genommen wird Wasser von der Erdoberfläche entnommen und in die Atmosphäre geblasen.
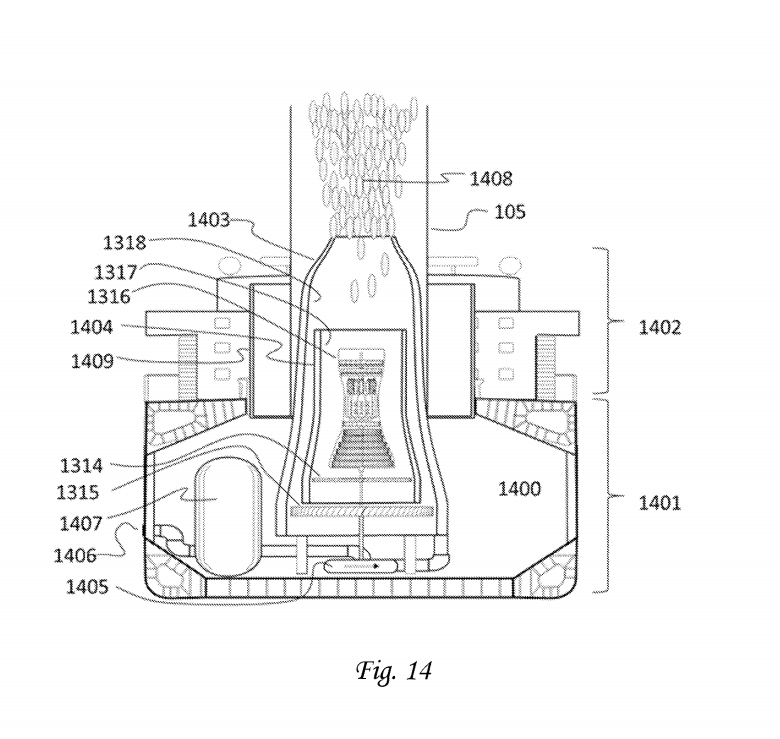
Methode und Apparatur, um einen Bereich der Erdatmosphäre, Ionosphäre und Magnetosphäre zu verändern, 1985
Das Patent ist auch als HAARP/Eastlund-Patent bekannt, letzteres, weil der Name des einreichenden Erfinders Bernard J. Eastlund lautet.
Ein Verfahren und eine Vorrichtung zur Veränderung mindestens eines ausgewählten Bereichs, der normalerweise über der Erdoberfläche liegt. Die Region wird durch Elektronenzyklotronresonanzerwärmung angeregt, um dadurch die Dichte geladener Teilchen zu erhöhen. In einer Ausführungsform wird zirkular polarisierte elektromagnetische Strahlung nach oben in einer Richtung übertragen, die im Wesentlichen parallel zu und entlang einer Feldlinie verläuft, die sich durch den zu verändernden Plasmabereich erstreckt. Die Strahlung wird mit einer Frequenz gesendet, die die Elektronenzyklotronresonanz anregt, um die geladenen Teilchen zu erhitzen und zu beschleunigen. Dieser Energieanstieg kann zur Ionisierung neutraler Teilchen führen, die dann als Teil der Region absorbiert werden, wodurch die geladene Teilchendichte der Region erhöht wird.
Künstlicher Regen durch Hochenergie-Laser, 2020
Die vorliegende Erfindung stellt ein System und eine Methodik zur künstlichen Regenerzeugung unter Verwendung eines Fernsteuerungssystems für Drohnenflugzeuge oder eines unbemannten Luftfahrzeugs unter Verwendung des Prinzips der endothermen Reaktion bereit. Das mit einer Pentax-Digitalkamera ausgestattete Mega-UAV wird für die Aufnahme hochauflösender Bilder auf Abruf verwendet. Das Mega-UAV wird durch einen Autopiloten zusammen mit vorprogrammierter Bodenkontrollsoftware gesteuert oder kann manuell mit einem einfachen Joystick im Funkfrequenzbereich gestartet werden. Um den Ionisierungsprozess auszulösen, ist das UAV mit einem Plasmafrequenz-Freisetzungssystem ausgestattet und wird in das Innere einer Wolkenmasse geschickt. Das UAV-System dringt tief in die Wolkenmasse ein und gibt einen einzelnen Hochleistungs-Laserimpuls in die Atmosphäre ab. Drohnensysteme werden verwendet, um durch Windkraft Beschleunigung und Turbulenzen zu erzeugen, und winzige Wasserpartikel kollidieren und werden zu größeren Regentropfen. Solche größeren Regentropfen dienen als Keim für die Bildung weiterer Regentropfen und es kommt zu Regen. Das Senden des UAV in die Wolke trägt dazu bei, das Risiko eines natürlichen Blitzeinschlags auf den Boden zu vermeiden und das Risiko einer Schädigung von Lebewesen zu optimieren.
- 0462795 – July 16, 1891 – Method Of Producing Rain-Fall
- 803180 – October 31, 1905 – Means for Producing High Potential Electrical Discharges
- 1103490 – August 6, 1913 – Rain-Maker
- 1225521 – September 4, 1915 – Protecting From Poisonous Gas In Warfare
- 1279823 – September 24, 1918 – Process and Apparatus for Causing Precipitation by Coalescence of Aqueous Particles Contained in the Atmosphere
- 1284982 – November 19, 1918 – Process and Apparatus for Procuring and Stimulating Rainfall
- 1338343 – April 27, 1920 – Process And Apparatus For The Production of Intense Artificial Clouds, Fogs, or Mists
- 1358084 – November 9, 1920 – Method of Producing Fog-Screens
- 1619183 – March 1, 1927 – Process of Producing Smoke Clouds From Moving Aircraft
- 1665267 – April 10, 1928 – Process of Producing Artificial Fogs
- 1892132 – December 27, 1932 – Atomizing Attachment For Airplane Engine Exhausts
- 1895765 – January 31, 1933 – Artificial Production of Fog
- 1928963 – October 3, 1933 – Electrical System And Method
- 1957075 – May 1, 1934 – Airplane Spray Equipment
- 1993316 – March 5, 1935 – Apparatus for and Method of Producing Oil Fog
- 2052626 – September 1, 1936 – Method of Dispelling Fog
- 2097581 – November 2, 1937 – Electric Stream Generator – Referenced in 3990987
- 2173756 – September 19, 1939 – Process of Producing Fog or Mist by Partial and Flameless Combustion
- 2352677 – July 4, 1944 – Artificial Fog Production
- 2476171 – July 18, 1945 – Smoke Screen Generator
- 2409201 – October 15, 1946 – Smoke Producing Mixture
- 2480967 – September 6, 1949 – Aerial Discharge Device
- 2527230 – October 24, 1950 – Method of Crystal Formation and Precipitation
- 2527231 – October 24, 1950 – Method of Generating Silver Iodide Smoke
- 2550324 – April 24, 1951 – Process For Controlling Weather
- 2582678 – June 15, 1952 – Material Disseminating Apparatus For Airplanes
- 2611992 – September 30, 1952 – Engine Exhaust Operated Fluent Material Distributor
- 2614083 – October 14, 1952 – Metal Chloride Screening Smoke Mixture
- 2633455 – March 31, 1953 – Smoke Generator
- 2688069 – August 31, 1954 – Steam Generator – Referenced in 3990987
- 2721495 – October 25, 1955 – Method And Apparatus For Detecting Minute Crystal Forming Particles
Suspended in a Gaseous Atmosphere - 2730402 – January 10, 1956 – Controllable Dispersal Device
- 2903188 – April 2, 1956 – Control of Tropical Cyclone Formation
- 2756097 – July 24, 1956 – Process for Weather Control
- 2801322 – July 30, 1957 – Decomposition Chamber for Monopropellant Fuel – Referenced in 3990987
- 2835530 – May 20, 1958 – Process for the Condensation of Atmospheric Humidity and Dissolution of Fog
- 2871344 – January 27, 1959 – Long Distance Communication System
- 2881335 – April 7, 1959 – Generation of Electrical Fields
- 2908442 – October 13, 1959 – Method For Dispersing Natural Atmospheric Fogs And Clouds
- 2962450 – November 29, 1960 – Fog Dispelling Composition
- 2963975 – December 13, 1960 – Cloud Seeding Carbon Dioxide Bullet
- 3019989 – February 6, 1962 – Atmospheric Space Charge Modification
- 2986360 – May 30, 1962 – Aerial Insecticide Dusting Device
- 3046168 – July 24, 1962 – Chemically Produced Colored Smokes
- 3056556 – October 2, 1962 – Method of Artificially Influencing the Weather
- 3126155 – March 24, 1964 – Silver Iodide Cloud Seeding Generator
- 3127107 – March 31, 1964 – Generation of Ice-Nucleating Crystals
- 3131131 – April 28, 1964 – Electrostatic Mixing in Microbial Conversions
- 3140207 – July 7, 1964 – Pyrotechnic Composition
- 3174150 – March 16, 1965 – Self-Focusing Antenna System
- 3234357 – February 8, 1966 – Electrically Heated Smoke Producing Device
- 3274035 – September 20, 1966 – Metallic Composition For Production of Hydroscopic Smoke
- 3284005 – November 8,1966 – Weather Control by Artificial Means
- 3300721 – January 24, 1967 – Means For Communication Through a Layer of Ionized Gases
- 3313487 – April 11, 1967 – Cloud Seeding Apparatus
- 3338476 – August 29, 1967 – Heating Device For Use With Aerosol Containers
- 3375148 – March 26, 1968 – Pyrotechnics Comprising Silver Iodate, Ammonium Nitrate, Nitrocellulose and Nitrate Esters
- 3378201 – April 16, 1968 – Method for Precipitating Atmospheric Water Masses
- 3410489 – November 12, 1968 – Automatically Adjustable Airfoil Spray System With Pump
- 3418184 – December 24, 1968 – Smoke Producing Propellant
- 3429507 – February 25, 1969 – Rainmaker
- 3432208 – November 7, 1967 – Fluidized Particle Dispenser
- 3441214 – April 29, 1969 – Method And Apparatus For Seeding Clouds
- 3445844 – May 20, 1969 – Trapped Electromagnetic Radiation Communications System
- 3456880 – July 22, 1969 – Method Of Producing Precipitation From The Atmosphere
- 3518670 – June 30, 1970 – Artificial Ion Cloud
- 3517512 – June 30, 1970 – Apparatus for Suppressing Contrails
- 3534906 – October 20, 1970 – Control of Atmospheric Particles
- 3545677 – December 8, 1970 – Method of Cloud Seeding
- 3564253 – February 16, 1971 – System And Method For Irradiation Of Planet Surface Areas
- 3587966 – June 28, 1971 – Freezing Nucleation
- 3595477 – July 27, 1971 – Fog Dispersing Method and Compositions
- 3601312 – August 24, 1971 – Methods of Increasing The Likelihood oF Precipitation By The Artificial Introduction Of Sea Water Vapor Into The Atmosphere Winward Of An Air Lift Region
- 3608810 – September 28, 1971 – Methods of Treating Atmospheric Conditions
- 3608820– September 20, 1971 – Treatment of Atmospheric Conditions by Intermittent Dispensing of Materials Therein
- 3613992 – October 19, 1971 – Weather Modification Method
- 3630950 – December 28, 1971 – Combustible Compositions For Generating Aerosols, Particularly Suitable For Cloud Modification And Weather Control And Aerosolization Process
- USRE29142 – May 22, 1973 – Combustible compositions for generating aerosols, particularly suitable for cloud modification and weather control and aerosolization process
- 3659785 – December 8, 1971 – Weather Modification Utilizing Microencapsulated Material
- 3666176 – March 3, 1972 – Solar Temperature Inversion Device
- 3677840 – July 18, 1972 – Pyrotechnics Comprising Oxide of Silver For Weather Modification Use
- 3690552 – September 12, 1972 – Fog Dispersal
- 3722183 – March 27, 1973 – Device For Clearing Impurities From The Atmosphere
- 3748278 – July 24, 1973 – Process and Agents Having an Influence on the Weather
- 3751913 – August 14, 1973 – Barium Release System
- 3769107 – October 30, 1973 – Pyrotechnic Composition For Generating Lead Based Smoke
- 3784099 – January 8, 1974 – Air Pollution Control Method
- 3785557 – January 15, 1974 – Cloud Seeding System
- 3788543 – January 29, 1974 – Uniform Size Particle Generator
- 3795626 – March 5, 1974 – Weather Modification Process
- 3802971 – April 9, 1974 – Pyrotechnic Formulations for Weather Modification Comprising a Mixture of Iodates
- 3808595 – April 30, 1974 – Chaff Dispensing System
- 3813875 – June 4, 1974 – Rocket Having Barium Release System to Create Ion Clouds In The Upper Atmosphere
- 3835059 – September 10, 1974 – Methods of Generating Ice Nuclei Smoke Particles For Weather Modification And Apparatus Therefore
- 3835293 – September 10, 1974 – Electrical Heating Apparatus For Generating Super Heated Vapors
- 3858805 – January 7, 1975 – Ice Nucleation by Micas
- 3877642 – April 15, 1975 – Freezing Nucleant
- 3882393 – May 6, 1975 – Communications System Utilizing Modulation of The Characteristic Polarization of The Ionosphere
- 3887580 – June 3, 1975 – Method of Crystallization of Water in Supercooled Clouds and Fogs and Reagent Useful in Said Method
- 3896993 – July 29, 1975 – Process For Local Modification of Fog And Clouds For Triggering Their Precipitation And For Hindering The Development of Hail Producing Clouds
- 3899129 – August 12, 1975 – Apparatus for generating ice nuclei smoke particles for weather modification
- 3899144 – August 12, 1975 – Powder contrail generation
- 3915379 – October 28, 1975 – Method of Controlling Weather
- 3940059 – February 24, 1976 – Method For Fog Dispersion
- 3940060 – February 24, 1976 – Vortex Ring Generator
- 3990987 – November 9, 1976 – Smoke generator
- 3992628 – November 16, 1976 – Countermeasure system for laser radiation
- 3994437 – November 30, 1976 – Broadcast dissemination of trace quantities of biologically active chemicals
- 4042196 – August 16, 1977 – Method and apparatus for triggering a substantial change in earth characteristics and measuring earth changes
- RE29,142 – February 22, 1977 – Combustible compositions for generating aerosols, particularly suitable for cloud modification and weather control and aerosolization process
- 4009828 – March 1 1977 – Organic Nucleating Agent for both Warm and Cold Clouds
- 4035726 – July 12, 1977 – Method of controlling and/or improving high-latitude and other communications or radio wave surveillance systems by partial control of radio wave et al
- 4096005 – June 20, 1978 – Pyrotechnic Cloud Seeding Composition
- 4129252 – December 12, 1978 – Method and apparatus for production of seeding materials
- 4141274 – February 27, 1979 – Weather modification automatic cartridge dispenser
- 4167008 – September 4, 1979 – Fluid bed chaff dispenser
- 4347284 – August 31, 1982 – White cover sheet material capable of reflecting ultraviolet rays
- 4362271 – December 7, 1982 – Procedure for the artificial modification of atmospheric precipitation as well as compounds with a dimethyl sulfoxide base for use in carrying out said procedure
- 4373391 – February 15, 1983 – Relative Humidity Sensitive Material
- 4396152 – August 2, 1983 – Aerosol Dispenser System
- 4402480 – September 6, 1983 – Atmosphere modification satellite
- 4412654 – November 1, 1983 – Laminar microjet atomizer and method of aerial spraying of liquids
- 4415265 – November 15, 1983 – Method and apparatus for aerosol particle absorption spectroscopy
- 4470544 – September 11, 1984 – Method of and Means for weather modification
- 4475927 – October 9, 1984 – Bipolar Fog Abatement System
- 4600147 – July 15, 1986 – Liquid propane generator for cloud seeding apparatus
- 4633714 – January 6, 1987 – Aerosol particle charge and size analyzer
- 4643355 – February 17, 1987 – Method and apparatus for modification of climatic conditions
- 4653690 – March 31, 1987 – Method of producing cumulus clouds
- 4684063 – August 4, 1987 – Particulates generation and removal
- 4686605 – August 11, 1987 Method and apparatus for altering a region in the earth’s atmosphere, ionosphere, and/or magnetosphere
- 4704942 – November 10, 1987 – Charged Aerosol
- 4712155 – December 8, 1987 – Method and apparatus for creating an artificial electron cyclotron heating region of plasma
- 4744919 – May 17, 1988 – Method of dispersing particulate aerosol tracer
- 4766725 – August 30, 1988 – Method of suppressing formation of contrails and solution therefor
- 4829838 – May 16, 1989 – Method and apparatus for the measurement of the size of particles entrained in a gas
- 4836086 – June 6, 1989 – Apparatus and method for the mixing and diffusion of warm and cold air for dissolving fog
- 4873928 – October 17, 1989 – Nuclear-sized explosions without radiation
- 4948257 – August 14, 1990 – Laser optical measuring device and method for stabilizing fringe pattern spacing
- 1338343– August 14, 1990 – Process and Apparatus for the production of intense artificial Fog
- 4999637 – March 12, 1991 – Creation of artificial ionization clouds above the earth
- 5003186 – March 26, 1991 – Stratospheric Welsbach seeding for reduction of global warming
- 5005355 – April 9, 1991 – Method of suppressing formation of contrails and solution therefor
- 5038664 – August 13, 1991 – Method for producing a shell of relativistic particles at an altitude above the earths surface
- 5041760 – August 20, 1991 – Method and apparatus for generating and utilizing a compound plasma configuration
- 5041834 – August 20, 1991 – Artificial ionospheric mirror composed of a plasma layer which can be tilted
- 5056357 – October 15, 1991- Acoustic method for measuring properties of a mobile medium
- 5059909 – October 22, 1991 – Determination of particle size and electrical charge
- 5104069 – April 14, 1992 – Apparatus and method for ejecting matter from an aircraft
- 5110502 – May 5, 1992 – Method of suppressing formation of contrails and solution therefor
- 5156802 – October 20, 1992 – Inspection of fuel particles with acoustics
- 5174498 – December 29, 1992 – Cloud Seeding
- 5148173 – September 15, 1992 – Millimeter wave screening cloud and method
- 5242820 – September 7, 1993 – Army Mycoplasma Patent Patent
- 5245290 – September 14, 1993 – Device for determining the size and charge of colloidal particles by measuring electroacoustic effect
- 5286979 – February 15, 1994 – Process for absorbing ultraviolet radiation using dispersed melanin
- 5296910 – March 22, 1994 – Method and apparatus for particle analysis
- 5327222 – July 5, 1994 – Displacement information detecting apparatus
- 5357865 – October 25, 1994 – Method of cloud seeding
- 5360162 – November 1, 1994 – Method and composition for precipitation of atmospheric water
- 5383024 – January 17, 1995 – Optical wet steam monitor
- 5425413 – June 20, 1995 – Method to hinder the formation and to break-up overhead atmospheric inversions, enhance ground level air circulation and improve urban air quality
- 5434667 – July 18, 1995 – Characterization of particles by modulated dynamic light scattering
- 5436039 – July 25, 1995 – Artificial Snow in an Aggregate Form of Snow Granules
- 5441200 – August 15, 1995 – Tropical cyclone disruption
- 5492274 – February 20, 1996 – Method of and Means for Weather Modification
- 5546183 – August, 13, 1996 – LIDAR Droplet Size Monitor for In-Flight Measurement of Aircraft Engine Exhaust Contrails, Droplets and Aerosols
- 5556029 – September 17, 1996 – Method of hydrometeor dissipation (clouds)
- 5628455 – May 13, 1997 – Method and apparatus for modification of supercooled fog
- 5631414 – May 20, 1997 – Method and device for remote diagnostics of ocean-atmosphere system state
- 5639441 – June 17, 1997 – Methods for fine particle formation
- 5762298 – June 9, 1998 – Use of artificial satellites in earth orbits adaptively to modify the effect that solar radiation would otherwise have on earth’s weather
- 5800481 – September 1, 1998 – Thermal excitation of sensory resonances
- 5912396 – June 15, 1999 – System and method for remediation of selected atmospheric conditions
- 5922976 – July 13, 1999 – Method of measuring aerosol particles using automated mobility-classified aerosol detector
- 5949001 – September 7, 1999 – Method for aerodynamic particle size analysis
- 5984239 – November 16, 1999 – Weather modification by artificial satellites
- 6025402 – February 15, 2000 – Chemical composition for effectuating a reduction of visibility obscuration, and a detoxifixation of fumes and chemical fogs in spaces of fire origin
- 6030506 – February 29, 2000 – Preparation of independently generated highly reactive chemical species
- 6034073 – March 7, 2000 – Solvent detergent emulsions having antiviral activity
- 6045089 – April 4, 2000 – Solar-powered airplane
- 6056203 – May 2, 2000 – Method and apparatus for modifying supercooled clouds
- 6315213B1 – June 21, 2000 – Method of modifying weather
- 6110590 – August 29, 2000 – Synthetically spun silk nanofibers and a process for making the same
- 6263744 – July 24, 2001 – Automated mobility-classified-aerosol detector
- 6281972 – August 28, 2001 – Method and apparatus for measuring particle-size distribution
- 20030085296 – November 2, 2001 – Hurricane and tornado control device
- 6315213 – November 13, 2001 – Method of modifying weather
- 2002009338 – January 24, 2002 – Influencing Weather Patterns by way of Altering Surface or Subsurface Ocean Water Temperatures
- 20020008155 – January 24, 2002 – Method and System for Hurricane Control
- 6382526 – May 7, 2002 – Process and apparatus for the production of nanofibers
- 6408704 – June 25, 2002 – Aerodynamic particle size analysis method and apparatus
- 6412416 – July 2, 2002 – Propellant-based aerosol generation devices and method
- 6520425 – February 18, 2003 – Process and apparatus for the production of nanofibers
- 6539812 – April 1, 2003 – System for measuring the flow-rate of a gas by means of ultrasound
- 6553849 – April 29, 2003 – Electrodynamic particle size analyzer
- 6569393 – May 27, 2003 – Method And Device For Cleaning The Atmosphere
- 20040060994 – April 1, 2004 – Method for Influencing Atmospheric Formations
- 20040074980 – April 22, 2004 – Method and Device for Generating a Liquid Mist
- 0056705 A1 – March 17, 2005 – Weather Modification by Royal Rainmaking Technology
- 6890497 – May 10, 2005 – Method For Extracting And Sequestering Carbon Dioxide
- 2446250 – January 4, 2007 – A dust or particle-based solar shield to counteract global warming
- 20070056436 – March 15, 2007 – Challenger to Natural Twisters, Technology
- 20070114298 – May 24, 2007 – Hurricane Abatement Method and System
- 20070158449 – July 12, 2007- Tropical Hurricane Control System
- 20070215946 – September 20, 2007 – Broadband Communications System via Reflection from Artificial Ionized Plasma Patterns in the Atmosphere
- 7965488 – November 9, 2007 – Methods Of Removing Aerosols From The Atmosphere
- 8048309 – August 28, 2008 – Seawater-Based Carbon Dioxide Disposal
- 20100072297 – September 24, 2008 – Method for controlling hurricanes
- 7434524 – October 14, 2008 – Machine to Get Rid of Hurricanes
- 8012453 – October 27, 2008 – Carbon Sequestration And Production Of Hydrogen And Hydride
- 20090008468 – January 8, 2009 – How to Tame Hurricanes and Typhoons with Available Technology
- 7520237 – April 21, 2009 – Hurricane Prevention System and Method
- 20090255999 – October 15, 2009 – Production or Distribution of Radiative Forcing Elements
- 20090290761 – November 26, 2009 – Upper Troposphere and Lower Stratosphere Wind Direction, Speed, and Turbidity Monitoring using Digital Imaging and Motion Tracking
- 7645326 – January 12, 2010 – RFID environmental manipulation
- 7655193 – February 2, 2010 – Apparatus For Extracting And Sequestering Carbon Dioxide
- 20100074390 – March 25, 2010 – Method for Weather Modification and Vapor Generator for Weather Modification
- 20100127224 – May 27, 2010 – Atmospheric Injection of Reflective Aerosol for Mitigating Global Warming
- 7748662 – July 6, 2010 – Aerial Delivery System
- 20100170958 – July 8, 2010 – Hurricane Mitigation by Combined Seeding with Condensation and Freezing Nuclei
- 20100252648 – October 7, 2010 – Climate Processor
- 20100282914 – November 11, 2010 – Enhanced Aerial Delivery System
- 20110005422 – January 13, 2011 – Method and Apparatus for Cooling a Planet
- 20110049257 – March 3, 2011 – Method and Apparatus for Local Modification of Atmosphere
- 20110101124 – May 5, 2011- Hurricane Abatement System and Method
- 2011073650 – June 23, 2011 – Atmospheric Delivery System
- 20110168797 – July 14, 2011 – Method of Weakening a Hurricane
- 20110174892 – July 21, 2011 – Apparatus and Related Methods for Weather Modification by Electrical Processes in the Atmosphere
- 20110198407 – August 18, 2011 – Method and Apparatus to Break Up or Annihilate Typhoons, Tornadoes, Cyclones or Hurricanes
- 20110204159 – August 25, 2011 – Weather Management Using Space-Based Power System
- 20110284649 – November 24, 2011 – Apparatus and Method for the Mitigation of Rotating Wind Storms
- 8079545 – December 20, 2011 – Ground based Manipulation and Control of Aerial Vehicle during nonflying operations
- 20120024971 – February 2, 2012 – Methods for Environmental Modification with Climate Control Materials and Coverings
- 8262314 – September 11, 2012 – Method for Decreasing the Intensity and Frequency of Tropical Storms or Hurricanes
- 0117003 – October 5, 2012 – Geoengineering Method Of Business Using Carbon Counterbalance Credits
- 20120267444 – October 25, 2012- Artificial Freezing Apparatus and Freezing Method Therefor
- 20120286096 – November 15, 2012 – Aerial Delivery Devices, Systems and Methods
- 20130008365 – January 10, 2013 – System and Method for Decreasing the Intensity and Frequency of Tropical Storms or Hurricanes
- 8373962 – February 12, 2013 – Charged seed cloud as a method for increasing particle collisions and for scavenging airborne biological agents and other contaminants
- 20130038063 – February 14, 2013 – Apparatus and Method for Inhibiting the Formation of Tropical Cyclones
- 201300043322 – February 21, 2013 – Processes and Apparatus for Reducing the Intensity of Tropical Cyclones
- 8402736 – March 26, 2013 – Method and Apparatus for Suppressing Aeroengine Contrails
- 8439278 – May 14, 2013 – Apparatus for Producing a Mass of Water Vapor, Apparatus for Producing, Moving, and Climbing a Mass of Water Vapor, and Method of Causing Artificial Stimulation of Rain
- 20130175352 – July 11, 2013 – Method to Influence the Direction of Travel of Hurricanes
- 20130186127 – July 25, 2013 – Ice Floater for Facilitating Ice-Freezing on Water Surface
- 20130206912 – August 15, 2013 – Moisture Dispersion
- 20140055876 – February 27, 2014 – Method for Controlling Land Surface Temperature using Stratospheric Airships and Reflector
- 20140131471 – May 15, 2014 – Apparatus to Channel Large Air Masses for Climate Modification
- 20140145002 – May 29, 2014 – System for Facilitating Cloud Formation and Cloud Precipitation
- 20140224894 – August 14, 2014 – Technique to Mitigate Storms using Arrays of Wind Turbines
- 8825241 – September 2, 2014 – Autonomous Wave-Powered substance Distribution Vessels for Fertilizing Plankton, Feeding Fish, and Sequestering Carbon from the Atmosphere
- 8944363 – February 3, 2015 – Production or Distribution of Radiative Forcing Agents
- 20150077737 – March 19 2015 – System and Methods for Monitoring an Environment
- 9002660 – April 7, 2015 – Device and Method for Determining and Indicating Climate-Relevant Effects of a Contrail Produced by an Airplane
- 20150230415 – August 20, 2015 – Methods for Decreasing Local Temperature using High Albedo Materials
- 20150337224 – November 26, 2015 – Microwave Acceleration of Carbon Gasification Reactions
- 9311539 – April 12, 2016 – Aircraft Contrail Detection
- 9429348 – August 30, 2016 – Method and Device for Producing Snow
- 9491911 – November 15, 2016 – Method for Modifying Environmental Conditions with Ring Comprised of Magnetic Material
- 9589473 – March 7, 2017 – Method and System for Automatically Displaying Flight Path, Seeding Path, and Weather Data
- 9715039 – July 25, 2017 – Apparatus and System for Smart Seeding within Cloud Formations
- 20170217587 – August 3, 2017 – Vehicles and Systems for Weather Modification
- 20170303479 – October 26, 2017 – Warm Cloud Catalyst, Preparation Method Therefor and Application Thereof
- 20180006422 – January 4, 2018 – Methods for Disrupting Hurricane Activity
- 20180006421 – January 4, 2018 – Methods for Disrupting Tornadic Activity
- 9924640 – March 27, 2018 – Modifying Sunlight Scatter in the Upper Atmosphere
- 20180217119 – August 2, 2018 – Process and Method for the Enhancement of Sequestering Atmospheric Carbon through Ocean Iron Fertilization, and Method for Calculating net Carbon Capture from said Process and Method
- 10189753 – January 29, 2019 – Fog-Generating Device Comprising a Reagent and Ignition Means
- 10314249 – June 11, 2019 – Systems and Methods of Inducing Rainfall
- 10375900 – August 13, 2019 – Rain Induced by Supercontinuum Laser Beams
- 10435165 – October 8, 2019 – Aircraft Electrically-Assisted Propulsion Control System
- 20190364748 – December 5, 2019 – Method and System for Expressing Airborne Cloud Seeding Line Considering Cloud Water
- 20200187430 – June 18, 2020 – Helical Artificial Generator of Tornado, Hurricane, Yellow Dust, and Typhoon
- 10701871 – July 7, 2020 – Systems for Maintaining and/or Decreasing Water Temperature using High Albedo Materials
- 20200233115 – July 23, 2020 – Method and System for Determining Cloud Seeding Potential
- 20200261939 – August 20, 2020 – Apparatus for Generating and Optically Characterizing an Aerosol
- 2020101897 – September 9, 2020 – Artificial Rainmaking by High Power Laser Initiation Endothermic Reactions through Drone Aircraft Remote Control System
- 20200288651 – September 17, 2020 – Methods for Cooling Water Temperature using High Albedo Materials
- 20200386970 – December 10, 2020 – Aerostatically Stabilized Atmospheric Reflector to Reduce Solar Irradiance
- 10888051 – January 12, 2021 – Intelligent Systems for Weather Modification Programs
- 20210037719 – February 11, 2021 – Planetary Weather Modification System
- 10941705 – March 9, 2021 – Hanson-Haber Aircraft Engine for the Production of Stratospheric Compounds and for the Creation of Atmospheric Reflectivity of Solar Radiation in the 555nm Range and to Increase Jet Engine Thrust and Fuel Economy through the Combustion of Ammonia and Ammonia By-Products
- 2021063943 – April 8, 2021 – Bacterial Preparations for Ice Nucleation
- 20210153442 – May 27, 2021 – Systems and Methods for Rain Cloud Initiation
- 20210163157 – June 3, 2021 – Artificial Ring, Solenoid System to Terraform
- 20210235638 – August 5, 2021 – Weather Management of Cyclonic Events
- 2021152336 – August 8, 2021 – Method of Cloud Seeding using Natural Ice Nucleating Agents
- 20210285851 – September 16, 2021- System for Sampling and Analyzing Contrails Generated by an Aircraft
- 20210289720 – September 23, 2021 – Systems and Methods for Producing Rain Clouds
- 2021105881 – October 21, 2021 – Process for Generating Marine Clouds and Ocean Microbubbles
- 20210329922 – October 28, 2021 – Compositions and Methods for Enhanced CO2 Capture and Storage
- 20210329852 – October 28, 2021 – Method for Preventing a Formation of, and/or for Dispersing, a Tropical Cyclone, and Arrangement Therefor
- 20210352856 – November 18, 2021 – Aerial Electrostatic System for Weather Modification
- 2021107294 – December 9, 2021 – Wind Turbines for Marine Cloud Brightening Dispersion
- 2022003028 – January 6, 2022 – Apparatus for Precipitation of Atmospheric Water
- 23220065599 – March 3, 2022 – Rocket for Artificial Rainfall using Ejection Hygroscopic Flare
- 11274534 – March 15, 2022 – Artificial rain to support water flooding in remote oil fields
- 20220113450 – April 14, 2022 – Calculation Method of Total Artificial Precipitation in Seeding Area Compared to Non-Seeding Area
- 2022094269 – May 5, 2022 – Reflective Hollow SRM Material and Methods
- 3994976 – May 11, 2022 – Apparatus for Electro-Spray Cloud Seeding
- 11330768 – May 17, 2022 – Systems and Methods for Producing Rain Clouds
- 20220268505 – August 25, 2022 – Method and Apparatus for Making Falling Snow
- 20220355925 – November 10, 2022 – Aeronautical Car and Associated Features









